how to test testicular torsion|testicular torsion signs on examination : wholesale Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Streaming sportif en direct et listes TV, scores en direct, résultats, tableaux, statistiques et actualités pour tous les sports majeurs, y compris le football, le basket-ball, le base-ball, le hockey, le football, le tennis, l'UFC, le NASCAR, la Formule 1. sport streaming, sp
{plog:ftitle_list}
web21 de jun. de 2023 · Welcome To LPSG Welcome to LPSG.com. If you are here because you are looking for the most amazing open-minded fun-spirited sexy adult community then you have found the right place. . Rodrigo Sampaio Expert Member. Media: 0. Joined Jan 9, 2020 Posts 14 Media 0 Likes 242 Points 38 Location Brasilia (Federal District, Brazil) .
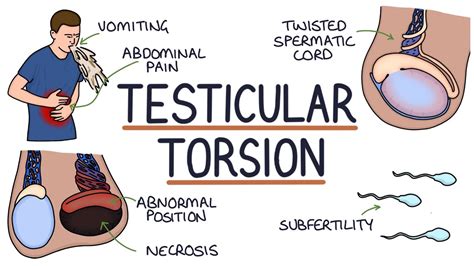
Like a cherry on its stem, the testicle hangs inside the scrotum on its arteries and veins. The scrotum is the skin covered sac that contains and protects the testicles. Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates and twists inside the scrotum, choking the blood flow through the arteries and veins. Without . See moreMales who experience sudden and severe pain in the scrotum, testicle ("ball"), belly or groin should be seen immediately by a doctor. Signs and symptoms of testicular torsion include: 1. Scrotal or testicular pain, often severe, that develops suddenly 2. Abdominal pain, . See moreWhile testicular torsion cannot be prevented, being aware of this emergency condition can help prevent permanent damage. Parents . See moreTesticular torsion is a medical emergency which requires immediate surgery (called an orchiopexy with detorsion) to restore blood flow to the testicles. Since it can take just four to six . See more
testicular torsion signs on examination
testicular torsion signs and symptoms
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing .
What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for .
Introduction. Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion . Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18, but it can occur at any age, even before birth. Testicular torsion usually requires emergency surgery. If treated . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and.Testicular torsion that goes on for more than a few hours can permanently damage the testicle, and a damaged testicle must be removed. . which probably won't happen if you have a testicular torsion. The doctor also might do tests . Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). Testicular torsion typically affects adolescents, although it can occur at all ages, including newborns and older adults. . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude . This is called testicular torsion. If testicular torsion occurs, it requires urgent medical attention. What causes testicular torsion and who is at risk? Testicular torsion can happen to boys and men of any age, but most cases occur in . This video contains a visual explanation of testicular torsion, aimed at helping students of medicine and healthcare professionals prepare for exams. Written.
testicular torsion prognosis
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .
This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. How is testicular torsion treated in a child? Testicular torsion often needs to be treated right away. The more severe the torsion, the more quickly treatment is needed. In some cases, the torsion may be untwisted by hand.↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .
Testicular self-exams (TSE) can help you check for things like cancer. Although testicular cancer is rare in teenage guys, overall it is the most common cancer in males between the ages of 15 and 35. It's important to try to do a TSE every month so you can become familiar with the normal size and .
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test . How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age. Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. It needs urgent medical attention to restore blood flow and prevent loss of the testicle. . urine or blood tests to check for .
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency when a testicle twists around the spermatic cord, cutting off the blood supply. While it can occur without pain, most people experience severe pain in the .Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required .What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when one of your testicles twists around. Each testicle is attached to a spermatic cord, which contains blood vessels that carry blood to the testicle. In testicular torsion, this becomes twisted (called torsion) and blocks the flow of blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is an emergency. Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult .
Testicular torsion can occur at any age, although it is more common in the first year of life and at puberty (peak age being 12-18 years). Testicular torsion can even occur before birth (during the prenatal period). Left testicle torsion is more common than right testicle torsion. The exact cause of testicular torsion is not known. Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound (Fig. 4) can be used to investigate potential compromised blood flow to the testis (if available, this test has a high sensitivity (89%) and . The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.I have broken bones, had a kidney stone, and had testicular torsion. Thankfully, all at separate times. If I had to pick one's pain to experience again, it'd definitely be long bone fracture over kidney stone over testicular torsion. If you're sitting down and thinking "hmmm, I wonder if I have testicular torsion?" - you don't.
Dr. Jason Fischer (http://www.twitter.com/eUSMD) describes a few techniques to identify testicular torsion and other issues using POCUS.*****P2Share is . Testicular torsion treatment. To diagnose testicular torsion, a doctor (often a urologist) evaluate the groin and scrotum area. The doctor will also check the abdomen. You may need an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. (An ultrasound creates an image with soundwaves). It allows the doctor to monitor blood flow and look for twisting.
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
O armazenamento ou acesso técnico é estritamente necessá.
how to test testicular torsion|testicular torsion signs on examination